Understanding What Xx Xx Is Equal To 2024 Means For Your Code And Systems Today
Have you ever faced a puzzle where a specific number, like 2024, becomes a key target for your projects or systems? Sometimes, you know, a particular value represents a goal, a benchmark, or even a version number in the world of technology. For many folks working with code and complex applications, reaching `xx xx is equal to 2024` might signify a successful optimization, a crucial update, or a new level of performance, actually.
This idea of a target number, like 2024, can appear in many forms, whether you are sorting out code definitions or fine-tuning how your applications use computer memory. We often work towards specific outcomes, making sure everything aligns just right. It's about getting things to work as expected, and sometimes even better, you know.
From clearing up warnings in your code to setting up memory for Java services, or even figuring out how reputation points work in a community, these seemingly small details can really add up. They all contribute to how well a system runs, and, in a way, they all push towards achieving those important numerical goals, like `xx xx is equal to 2024`, pretty much.
Table of Contents
- The Goal of 2024 in Software Development
- Code Definitions and File Types: Making Things Clear
- Tackling Application Memory Challenges
- The Importance of Community and Feedback
- Keeping Code Clean and Stable
- Frequently Asked Questions About Reaching 2024 Targets
- Moving Forward with Your 2024 Goals
The Goal of 2024 in Software Development
In the world of creating software, having a clear target is really useful, you know. When we talk about `xx xx is equal to 2024`, it could represent many things. It might be a version number for a new release, a performance score we are aiming for, or perhaps a count of successful operations in a given timeframe. Whatever it stands for, it suggests a point of completion or a desired state, you know, for our digital creations.
This target of 2024 could be a sign of a system running smoothly, with all its parts working together effectively. It could mean that our code is clean, our memory use is good, and our applications are giving users a great experience. Getting to this number often involves a lot of careful thought and precise adjustments, pretty much.
We often think about these kinds of numerical goals when we are trying to make things better. It's like having a clear destination on a map, which helps us plan our route and measure our progress. So, when we see `xx xx is equal to 2024`, it's a good reminder of what we are working towards, in a way.
Code Definitions and File Types: Making Things Clear
One fundamental part of any software project is how we organize our code. This organization helps us keep things tidy and makes it easier for others, or even our future selves, to pick up where we left off. It's a bit like having clear labels on everything in a workshop, actually.
Header Files and Source Files
When you are working with languages like C or C++, you often deal with different kinds of files. You might have seen files ending in `.h` or `.hpp` for your class definitions. These are header files, and they essentially tell other parts of your program what functions and variables are available. They are like the blueprints, you know, for your code's structures.
I used to think that it used to be that `.h` files were header files for C and C++. And that's largely true, but with C++ sometimes people prefer `.hpp` for C++-specific header content. This distinction helps keep things clear, especially in bigger projects. So what's the equivalent replacement for it if you're moving between older and newer ways of doing things? It's often about sticking to common practices for the language you are using, really.
The source files, often ending in `.cc` or `.cpp`, contain the actual instructions for your program. They are where the functions declared in the header files actually do their work. The difference between `.cc` and `.cpp` file suffix is mostly a matter of convention, with `.cpp` being very common. Clear definitions in these files contribute to a stable system, which might help us reach a goal like `xx xx is equal to 2024` in terms of code quality or successful compilation runs, for example.
Understanding File Suffixes
Knowing what each file suffix means is pretty important for organizing your project. It helps development tools know how to handle each file, and it helps other developers quickly understand what they are looking at. You have distinct categories of files, each with its own role, you know.
This careful naming and structuring of files can prevent many problems down the road. It means less time spent debugging and more time building new features. That sort of efficiency, you know, definitely helps in meeting project targets, potentially even contributing to a `xx xx is equal to 2024` milestone for a project's completion or stability.
Tackling Application Memory Challenges
One of the biggest concerns for any application is how it uses computer memory. If an application is not careful with its memory, it can slow down, or even crash. This is especially true for large applications that handle a lot of information, as a matter of fact.
Java Heap Management
Consider an application that has a heap of 8GB and creates a lot of short-living objects. Short-living objects are temporary pieces of data that are created and then quickly discarded. If too many of these are made too fast, the system spends a lot of time cleaning them up, which can really slow things down. I noticed that it often struggles with this, you know.
I have a Java service that currently runs with a 14GB heap. Managing such a large heap means paying close attention to how memory is allocated and released. Poor memory handling can prevent your application from hitting those important performance goals, perhaps keeping it from reaching a `xx xx is equal to 2024` operations per second rate, for instance.
JVM Memory Settings
For Java applications, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) has specific settings to help manage memory. The flag `xmx` specifies the maximum memory allocation pool for a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), while `xms` specifies the initial memory allocation pool. Setting these values correctly is really important for performance, actually.
If `xms` is too low, the JVM might spend a lot of time increasing its memory pool, which can cause pauses. If `xmx` is too high, it might take up too much system memory, leaving less for other applications. Finding the right balance is a key part of optimization. As of Java 8u191, you now have options that provide even more fine-grained control over memory settings, which can be very helpful, you know, for achieving specific performance targets like `xx xx is equal to 2024` for throughput or response times.
For more detailed information on Java memory settings and optimization, you might want to look at official Java documentation on garbage collection tuning. This sort of detailed guidance is very useful when you're trying to squeeze every bit of performance out of your system, pretty much.
Benchmarking for Performance
To really know if your memory adjustments are working, you need to measure them. I am running some micro benchmarks on Java list iteration code. Benchmarking involves running small, focused tests to see how quickly certain parts of your code perform. This helps identify bottlenecks and areas that need improvement, you know.
If your list iteration code is slow, it could be because of how memory is being used, or perhaps the way the list is structured. Improving these small parts can have a big impact on the overall speed of your application. This work is directly related to hitting performance goals, like achieving a specific number of iterations, or perhaps a `xx xx is equal to 2024` millisecond execution time for a critical process, in a way.
Learn more about performance tuning on our site, and link to this page for more insights into code optimization.
The Importance of Community and Feedback
Beyond the technical details of code and memory, there's also the human element of software development. Communities play a big role in helping developers learn and solve problems, too it's almost.
Reputation and Upvoting
On many online platforms, like forums or Q&A sites, you'll find systems for reputation. You'll need to complete a few actions and gain 15 reputation points before being able to upvote, for example. Upvoting indicates when questions and answers are useful, which helps good information stand out, you know.
What's reputation and how do I get it? What's reputation and how do I get it? These are common questions. Reputation often grows when you provide helpful answers or ask clear questions that others find useful. This system helps build a reliable knowledge base. The collective effort of a community, sharing solutions and best practices, can indirectly help everyone reach their technical goals, perhaps even ensuring that our systems are stable enough to consistently hit a `xx xx is equal to 2024` uptime target, actually.
This collaborative spirit is a pretty big part of how many technical problems get solved. When people share their experiences with things like memory allocation or code definitions, it helps others avoid similar issues. It's a way of making sure everyone is working with the best information available, you know.
Keeping Code Clean and Stable
No matter how well you manage memory or how clear your file definitions are, problems can still pop up. That's why paying attention to warnings and errors is so important. They are like little alerts telling you something might not be quite right, for instance.
All warnings were cleared except. This phrase suggests a diligent effort to clean up code, leaving only a few stubborn issues. Clearing warnings is a very important step towards making sure your software is reliable and performs well. Warnings, even if they don't stop your code from running, can point to potential problems that might show up later. Addressing them helps prevent bigger issues and keeps your application running smoothly, you know.
A system that consistently clears warnings and maintains high code quality is much more likely to meet its performance and stability goals. This kind of attention to detail helps ensure that your application can truly achieve something like `xx xx is equal to 2024` in terms of error-free operation or successful deployments. It’s about building a solid foundation, basically.
Frequently Asked Questions About Reaching 2024 Targets
Here are some common questions people have about setting and reaching specific numerical goals in their projects.
What does reaching a target value like 2024 mean in programming?
Reaching a target value like 2024 in programming can mean many things. It might represent a successful performance benchmark, like 2024 operations per second, or a version number for a software release. It could also be a count of successful test cases, or a specific metric for system stability, you
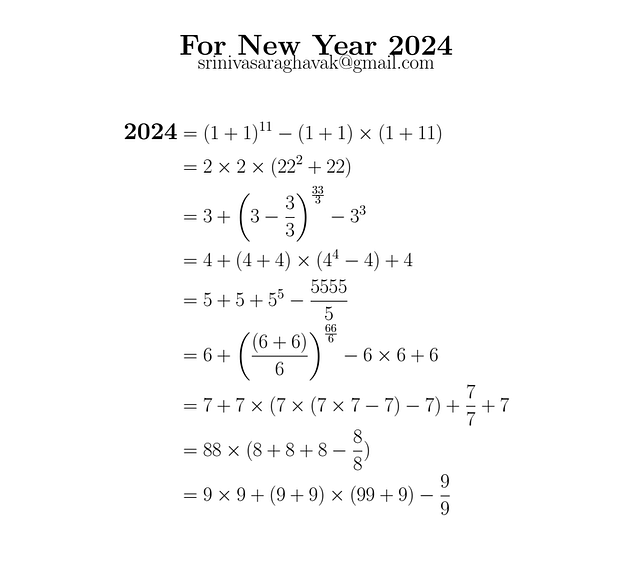
2024: A Mathematical Journey Into The New Year

IPL 2024 | David Warner Equals Chris Gayle's Record of Most Fifties in T20s
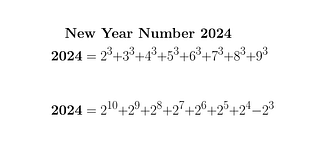
2024: A Mathematical Journey Into The New Year