Connect IoT Behind Router Raspberry Pi: Your Guide To A Smart, Secure Home
Ever wondered how to get your smart gadgets talking to each other, even when they are tucked away behind your home router? It is a common question, you know, especially when you are building a smart home or a cool automation project. Getting your Internet of Things, or IoT, devices to communicate reliably and safely from behind your network's protective wall, with a Raspberry Pi as your central brain, is what we are going to talk about today. It is a bit like learning how to use Connect's self-study resources; it takes a little effort, but the payoff is great.
Many folks, you see, want to keep their smart devices private and secure. They do not want everything on the internet for just anyone to find. Using a Raspberry Pi to manage these gadgets, while they stay inside your home network, offers a good balance of control and safety. This setup lets you build some pretty amazing things, too, from automated lights to smart garden systems, all without exposing every single device directly to the big, wide web. It is a clever way to keep things running smoothly, actually.
This guide will walk you through the how-to of connecting your IoT devices, using a Raspberry Pi as your hub, all while keeping them snug behind your router. We will cover why this setup is a smart move, the tools you will need, and several ways to access your creations from anywhere. So, if you have questions or need technical assistance with your home network, please feel free to read on; we are going to explore how to make your smart home dreams a reality.
Table of Contents
- What Does "Behind Your Router" Even Mean?
- Why You'd Want Your IoT Devices Behind the Router
- Your Raspberry Pi: The Smart Bridge
- Making Your IoT Devices Talk to the Pi
- Reaching Your IoT from Anywhere: The Remote Access Puzzle
- Security First: Keeping Your IoT Setup Safe
- Common Questions People Ask
- Putting It All Together: A Simple Example
- Your Next Steps for a Connected Home
What Does "Behind Your Router" Even Mean?
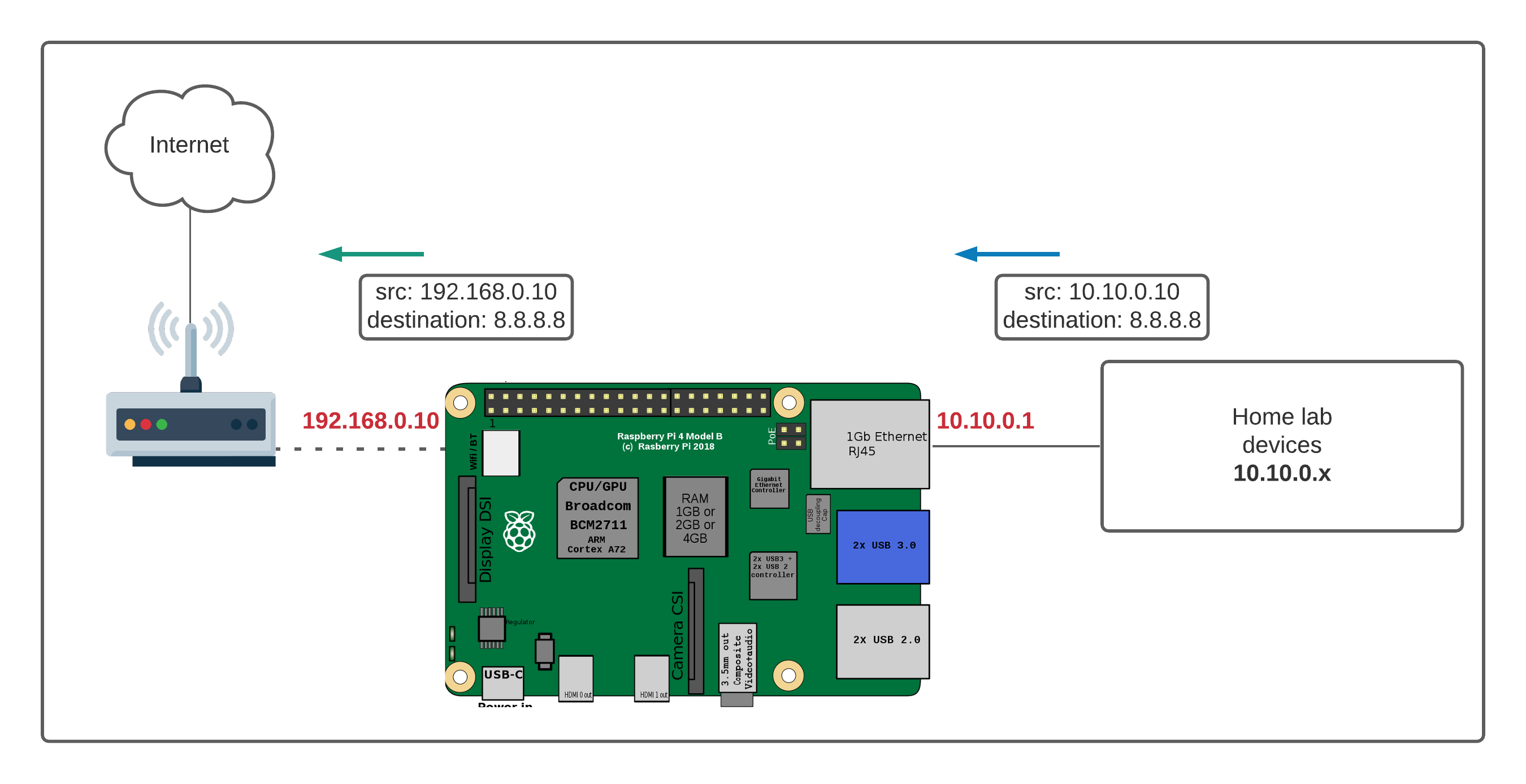
When we talk about devices being "behind your router," we are, you know, referring to them sitting on your local area network, or LAN. Your router acts as a gatekeeper. It gives each device inside your home a private address, like a room number in a big building. This private address is only visible to other devices within your home network. The outside world, the internet, only sees your router's single public address, which is like the building's street address, in a way.
This setup, called Network Address Translation or NAT, is actually a basic security feature. It hides your individual devices from direct access by anyone on the internet. Your router translates requests coming from the internet to the correct device inside your home, but only if it knows where to send them. This means, naturally, that without some special setup, devices outside your home cannot just "see" or talk to your IoT gadgets directly.
So, your IoT devices are, more or less, safe inside your network bubble. This is a good thing for security. But it also means you cannot easily access them from, say, your phone when you are away from home. This is the puzzle we are going to solve, you see, using your Raspberry Pi as a key part of the solution.
Why You'd Want Your IoT Devices Behind the Router
There are a few really good reasons to keep your smart gadgets tucked away on your home network. The first, and arguably the most important, is security. Many IoT devices, frankly, do not have the strongest security features built in. Exposing them directly to the internet can make them easy targets for bad actors. By keeping them behind your router, you add a layer of protection.
Another big reason is local control. When your devices communicate only within your home network, you are not relying on external cloud services. This can mean faster response times, more privacy, and continued operation even if your internet connection goes down. It gives you, you know, more direct power over your smart home, which is a pretty good feeling.
Also, it helps with network isolation. You might have some devices that you trust more than others. By keeping your less trusted IoT devices behind a Raspberry Pi gateway, you can, in some respects, limit their access to the rest of your home network. This is a smart way to manage potential risks. It is a bit like having different sections in a library; some books are for general access, others need special permission.
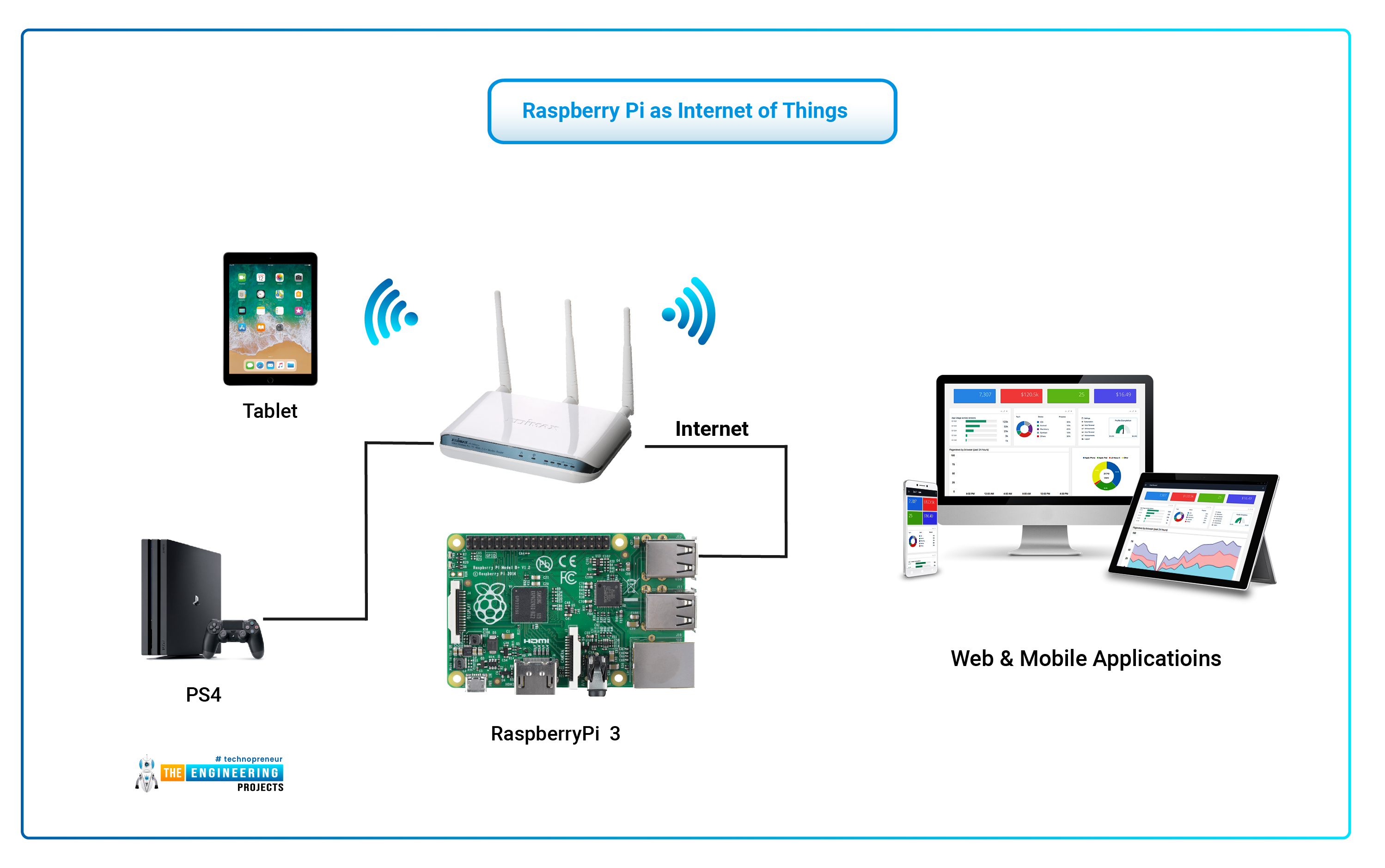
Your Raspberry Pi: The Smart Bridge
The Raspberry Pi is a small, affordable computer. It is really good for projects like this because it can run continuously and handle various tasks. For connecting IoT devices behind your router, the Pi acts as a central brain or a bridge. It can talk to your local devices and also, with some setup, communicate with the outside world on their behalf. This makes it, you know, an ideal hub for your smart home efforts.
It is almost like an instructor using Connect to manage courses and track student progress. Your Pi helps manage your devices and track their data. It brings all your different smart gadgets together, allowing them to work as one system. This is where the magic happens, actually, turning a collection of devices into a truly connected home.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi
First things first, you need to get your Raspberry Pi ready. This usually means installing an operating system, like Raspberry Pi OS, onto a microSD card. You can use a tool like Raspberry Pi Imager to do this, which makes the process fairly straightforward. Once the OS is on, you will need to boot up your Pi and connect it to your home network, usually via Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable.
After that, you will want to enable SSH, which lets you control your Pi from another computer on your network. This is a secure way to access your Pi without needing a screen or keyboard attached to it all the time. You will, you know, typically do this through the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool or by creating an empty file named `ssh` in the boot partition of your SD card. This basic setup is, in some respects, your foundation.
It is a good idea to update your Pi's software packages right away. You can do this by running a couple of commands in the terminal: `sudo apt update` and then `sudo apt upgrade`. This ensures you have the latest security patches and software versions, which is, you know, quite important for any device connected to your network. Just like any system, regular updates are key.
Essential Software for IoT Control
Once your Raspberry Pi is running, you will want to install some software to help it manage your IoT devices. One very common tool is MQTT, often implemented with a broker like Mosquitto. MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol. It lets your devices send small messages to the Pi, and the Pi can send messages back to them. It is, basically, a communication system for your smart things.
Another popular choice is Node-RED. This is a visual programming tool. You can drag and drop "nodes" to create flows that connect your devices, process data, and automate tasks. It is, in a way, very intuitive for building complex interactions without writing lots of code. Many people find it a great way to, you know, get started with automation.
For a full-fledged smart home hub, Home Assistant is a powerful option. It is an open-source platform that supports a huge number of devices and services. You install it on your Pi, and it gives you a web interface to control everything. It is, like, your central dashboard for all your smart home needs. Learning how to use Connect's self-study resources helps you master a platform, and Home Assistant is a platform worth mastering for your home.
Making Your IoT Devices Talk to the Pi
Now that your Raspberry Pi is ready, you need to get your actual IoT devices communicating with it. This usually happens locally, within your home network. The Pi acts as the listener and the speaker for these devices. It is, you know, the central point for all their chatter. There are a few common ways they can connect.
Many smart devices are designed to talk to a hub or a central controller. Your Raspberry Pi, running software like Home Assistant or a Mosquitto MQTT broker, fills that role perfectly. This local communication keeps your device data within your home, which is, you know, a big plus for privacy. It is pretty straightforward, actually, once you get the hang of it.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Connections
Most modern IoT devices use Wi-Fi to connect to your home network. Your Raspberry Pi, also connected to the same Wi-Fi, can then communicate with them. This is, basically, the most common setup. You just make sure both the Pi and your IoT gadgets are on the same Wi-Fi network, and then your Pi's software can discover and control them. It is, in some respects, quite simple.
Bluetooth is another option, especially for devices that are close to the Raspberry Pi. Things like smart temperature sensors or certain light bulbs might use Bluetooth Low Energy, or BLE. Your Raspberry Pi models often come with built-in Bluetooth, so it can, you know, talk directly to these devices. This can be good for lower power consumption, too, which is a nice benefit.
Other Protocols
Beyond Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, some IoT devices use other wireless protocols. Zigbee and Z-Wave are two popular ones. These often require a special USB dongle plugged into your Raspberry Pi. The dongle acts as a translator, letting your Pi communicate with these devices. This expands the range of gadgets your Pi can control, which is, you know, pretty handy.
For instance, if you have smart light switches that use Zigbee, you would plug a Zigbee USB stick into your Pi. Then, software like Home Assistant can use that stick to talk to the switches. It is, basically, like adding a new language to your Pi's vocabulary. This makes your Pi a very versatile smart home hub, able to, you know, connect to a wide variety of devices.
Reaching Your IoT from Anywhere: The Remote Access Puzzle
The real challenge, and what many people want to figure out, is how to access your Raspberry Pi and its connected IoT devices when you are not at home. Since your devices are behind your router, direct access from the internet is blocked. You need a way to, you know, securely punch a hole through that router's wall or, better yet, find a smarter path. There are several ways to do this, each with its own pros and cons.
Just as you might enter your user ID and password to access your account on a learning platform, you need a way to securely access your home network. This is where the different remote access methods come into play. We are looking for something that is, you know, both convenient and safe. It is a bit of a balancing act, really, between ease of use and keeping things locked down.
Method 1: Port Forwarding (Use with Caution!)
Port forwarding is, perhaps, the most direct way to allow outside access. You tell your router to send specific types of internet traffic to a specific device on your home network, like your Raspberry Pi. For example, you might forward port 80 to your Pi's IP address if you were running a web server. This, you know, creates a direct path from the internet to your Pi.
However, port forwarding comes with risks. It exposes your Raspberry Pi, or whatever device you forward ports to, directly to the internet. If there are any security flaws in the software running on your Pi, attackers could potentially exploit them. It is, basically, like leaving a door unlocked in your house. So, while it works, it is generally not recommended for most IoT setups unless you really know what you are doing and can keep your Pi very secure. You should, you know, always be aware of the terms of use and privacy policy for any service you expose.
How To Set Up RemoteIoT Behind Router Raspberry Pi: A Complete Guide
Raspberry Pi Remote IoT Free: Ultimate Guide & Setup

Mastering Control Raspberry Pi Behind Router For IoT Free Android: A Comprehensive Guide